Understanding Lymphedema Treatment: Options and Approaches
Lymphedema is a chronic condition affecting many people worldwide, especially those who have undergone surgery or radiation therapy for cancer. It occurs when the lymphatic system, which is in control of maintaining fluid balance in the body, becomes damaged or blocked, causing fluid to accumulate in the tissues and leading to swelling and discomfort. While there is no cure for lymphedema, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. This article explores some of the most common approaches to lymphedema treatment and how they work.
Compression Therapy
Compression therapy is the most widely used lymphedema treatment and involves applying pressure to the affected limb or area using specialized bandages, sleeves, or stockings. Compression therapy aims to reduce swelling by improving the flow of lymphatic fluid and preventing it from pooling in the tissues.
There are different levels of compression, ranging from mild to high, depending on the severity of the lymphedema. A healthcare professional will typically recommend the appropriate level of compression based on individual needs and circumstances.
Manual Lymphatic Drainage
Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) is a gentle massage technique that can help stimulate the lymphatic system and improve the flow of lymphatic fluid. It involves a series of rhythmic, circular movements that target specific body areas and is usually performed by a trained therapist.
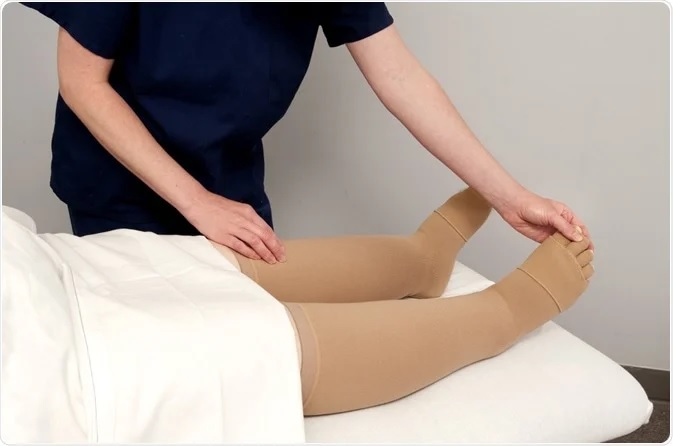
MLD can be used as a standalone treatment or in combination with compression therapy and is particularly effective for reducing swelling and improving mobility in the affected limb or area.
Exercise
Regular exercise can also play a crucial role in managing lymphedema, as it helps to improve circulation and prevent the buildup of lymphatic fluid. Depending on the severity of the condition, a healthcare professional may recommend specific exercises or a personalized exercise program tailored to the individual’s needs.
It’s important to note that people with lymphedema should avoid activities that may cause injury or trauma to the affected area, such as heavy lifting or high-impact sports.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be put forward to treat lymphedema. This can involve removing excess tissue or repairing damaged lymph vessels and is typically reserved for severe or advanced cases that do not respond to other treatments.
Lifestyle Changes
In addition to these treatment options, lifestyle changes can help manage lymphedema symptoms. This may involve maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding tight clothing or jewelry that may restrict circulation, and protecting the affected limb or area from injury or infection.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lymphedema is a condition that can be managed over time by combining different therapies and making some lifestyle changes. Working with a healthcare professional and following a personalized care plan can greatly improve the quality of life for those with lymphedema and reduce the chances of complication.

